Troubleshooting
This page covers some common troubleshooting tips for using the TSC library.
- 400000 Bad Request
- Logging REST API communication with Tableau Server
- Capture REST API communication with local proxy
400000 Bad Request
It’s not uncommon to receive a response error similar to the following:
400000: Bad Request
Payload is either malformed or incomplete
This type of response can be caused by several different problems communicating with the backend REST API. Try these steps to resolve the issue:
- Update to the latest release of the TSC library
- Adjust your code to always use the latest REST API version supported by the server
If the problem still persists, you can post an Issue with details to see if others can help. It might also be helpful to capture the REST API requests and responses as described next.
Logging REST API communication with Tableau Server
There may be cases where it’s helpful to inspect the REST API calls the TSC library is making and the responses coming back from Tableau Server. Some examples might be:
- The TSC library is throwing an error or the results are not coming through as expected
- The TSC library or the REST backend may have a bug which needs to be tracked down
To enable logging, add the following to your Python script ahead of making any TSC calls:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
filename="tsc.log", level="DEBUG")
Now when your script executes, you’ll see a set of debug messages in the tsc.log file. Each API call to the REST API will be included along with the XML responses. Depending on the problem being investigated, you can compare these requests/responses to the REST API documentation to track down the issue.
Capture REST API communication with local proxy
Another approach for inspecting REST API traffic is to use a local debugging proxy server like Fiddler Everywhere. Fiddler Everywhere is free for basic use and has versions for Mac, Windows and Linux.
These are the steps to send the API traffic through to a local proxy like Fiddler:
- Install Fiddler Everywhere and create a free account if needed
- Launch the Fiddler app and click the settings (gear) icon to enable Capture HTTPS traffic. (Do not click Trust root certificate.)
- Before running your script, set the following environment variables (on Windows, use SET commands instead):
export HTTP_PROXY=http://127.0.0.1:8866 export HTTPS_PROXY=http://127.0.0.1:8866 export CURL_CA_BUNDLE="" export PYTHONWARNINGS="ignore:Unverified HTTPS request" - Run your script
- Check Fiddler Everywhere for the results
The sample screenshot below shows the results of running a simple sign in/out sequence. The Capture pane includes one row for each HTTP request. Select the request to see the details on the right side: Request and Response.
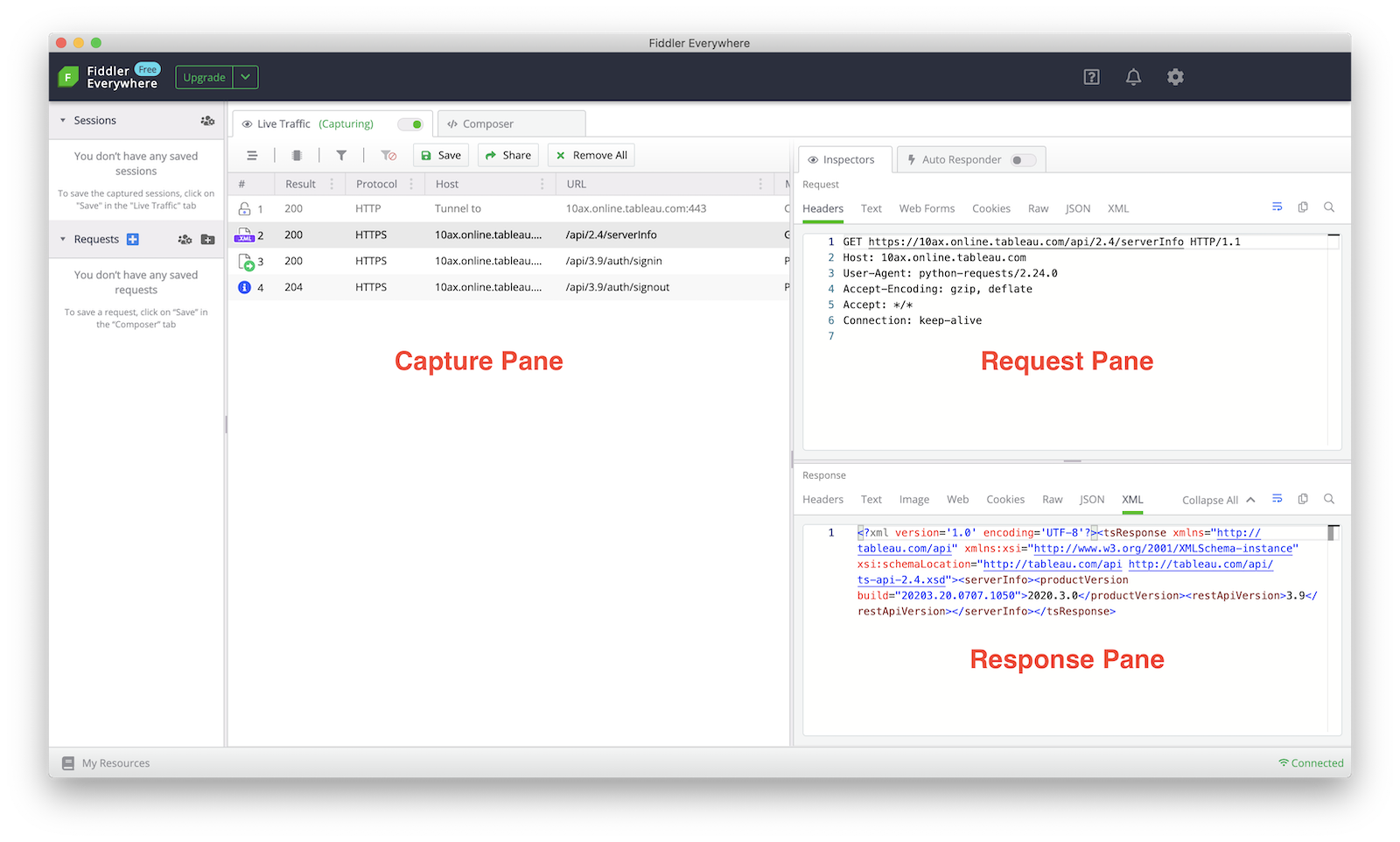
Proxy server applications other than Fiddler can be used as well. Just adjust the HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY environment variables to use the proper IP address and port number.